Gum inflammation in dogs
Inflammations of the gums – painful and dangerous
Tartar can cause gum infections which are extremely painful and may lead to your dog being unable to eat.
Gum inflammation often is only a precursor of periodontitis, a massive infection of the periodontal apparatus, that might cause bone resorption – and in some cases even results in the loss of the teeth.
Gum infections can attack the bone of the jaw and cause teeth to fall out – in some cases, all of them. That is why it is so important that gum infections are properly treated. Furthermore, the bacteria which cause tartar could migrate from the oral cavity into the blood vessels of the dog and thus damage internal organs such as the heart.
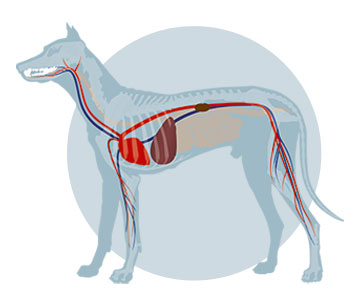
The picture shows the anatomical connection from the blood circulation between the internal organs and the muzzle of dogs. With this, entered bacteria can spread in the whole body.
The increased germ load has been poven to lead to inflammations of the internal organs such as the heart, kidneys and liver, as well as metabolic diseases. These are a threat to the dogs’s body and immune system and therefor are a high risk for the health.
That is why a preventive protection and an urgent treatment against tartar in dogs are essential.
Identifying gum inflammations (gingivitis)
Healthy gums are pink, wet, smooth and shiny. Depending on the fur colour or the breed, the gums can also be spotted or fully dark pigmented.
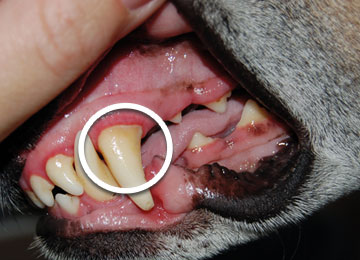
You can recognize a gum inflammation of dogs or cats by the red edges on the passage from teeth to gum.

How to recognize gum inflammations
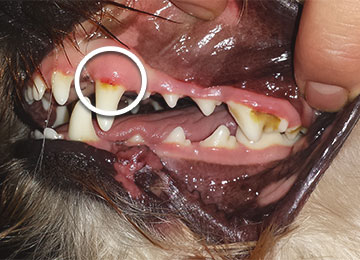
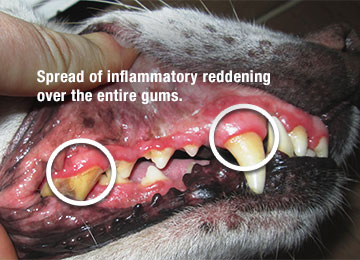
Depending on the extent, a gum inflammation can be apparent as a thin, red line along the passage up to a redness of the full gum. A light bleeding of the infected gum is also common. Gum inflammations also mostly produces unpleasant muzzle odour.
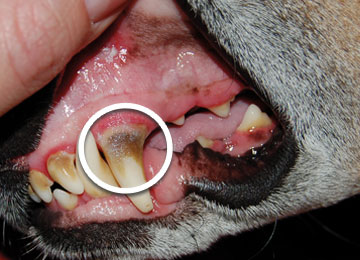
Before and after photos
With the following example, you can see how regular use of our OralClean+Care dental care can relieve gum inflammations, even over a short period of time.


 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 Français
Français


.png)


.png)

.png)